Before we dive into the recent advances in the field of computer vision, let’s cover a few basic ideas and some of the historical events that brought to deep learning and computer vision together.
Introduction to computer vision
Computer vision is the science that primarily aims to give computers the ability to understand and draw insights from images and videos. Computer vision makes it possible automate visual tasks like the extraction and analysis of useful information from images or videos. The secondary aim of computer vision systems is to improve the quality of images and videos.
Introduction to machine learning and deep learning
Machine learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that rely on a data-driven approach for decision-making instead of using a logical rule-based approach often based on first principles. Given a lot of high-quality data and by improving the algorithms machine learning systems have the ability to progressively improve their performance on a specific task. Deep learning is a subcategory of machine learning and focuses entirely on a set of mathematical algorithms that can be described as a network. Their inception was inspired by the biological neural networks found in the human brain and, similarly, artificial neural networks have millions of artificial synapses, which are represented mathematically by millions of simple linear algebraic equations.
Deep learning powered computer vision
Since 2012 deep learning neural networks have been the primary focus for computer vision and with good reason. The advantages of computer vision systems powered by deep learning are that they have a higher accuracy, are more flexible, and more tolerant of a high amount of variation in lighting conditions, viewpoint, scale, orientation, background clutter, intra-class variation, deformation and visual obstruction. But most importantly, they have enabled new use cases.
Early computer vision models relied on raw pixel data as the input to the machine learning model. However, raw pixel data alone is not sufficient to encompass the countless number of variations of an object in an image.
Deep learning powered computer vision is based on the idea that deep neural networks can extract and create task-specific features automatically during the training phase, which are then used to perform the Computer Vision task.
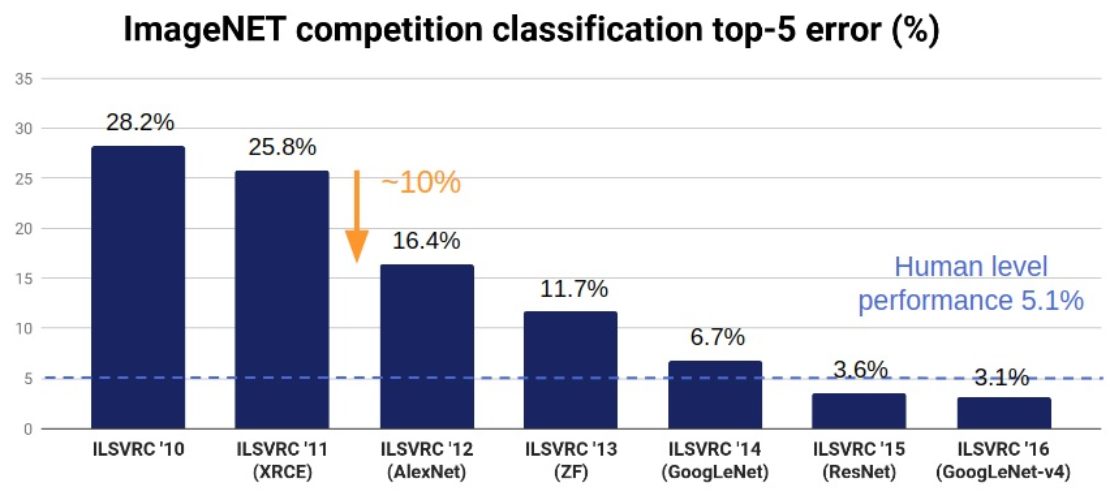
The following graph highlights some of the most important events in the 6-year history of deep learning and computer vision.
- The breakthrough caused by the introduction of deep neural networks 2012 lead to a roughly 10% decrease in image classification error (from 25.8% in 2011 to 16.4% in 2012).
- In 2015 the state of the art deep learning algorithms surpassed human level performance for image classification (5.1%, Russakovsky et al.) with an accuracy of 3.57%.
- Overall the introduction of deep neural networks resulted in a 10× reduction in image classification error (from 25.8% in 2011 to 2.3% in 2017).